Some bone interiors contain hemopoietic tissue which functions in – Some bone interiors contain hemopoietic tissue, a specialized tissue responsible for the production of blood cells. This tissue, found within the bone marrow, plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s blood supply and immune system.
Hemopoietic tissue is composed of various cell types, including stem cells, which give rise to all blood cells. The microenvironment within the bone marrow provides the necessary conditions for the growth, differentiation, and maturation of these cells.
Introduction: Some Bone Interiors Contain Hemopoietic Tissue Which Functions In
Hemopoietic tissue, also known as blood-forming tissue, is responsible for producing all types of blood cells. It is found in the bone marrow of certain bones and plays a vital role in the maintenance of blood cell homeostasis.
Bone marrow is a soft, spongy tissue located in the cavities of bones. It is the primary site of hemopoiesis, the process of blood cell production. Bone marrow contains a variety of cells, including stem cells, which are capable of differentiating into all types of blood cells.
Types of Hemopoietic Tissue

There are two main types of hemopoietic tissue: myeloid tissue and lymphoid tissue.
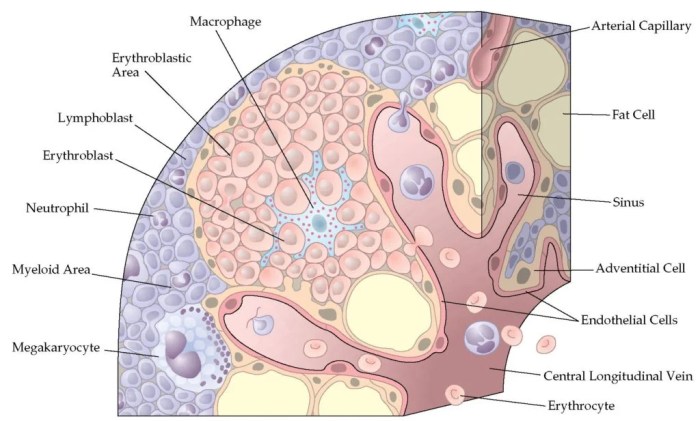
Myeloid Tissue, Some bone interiors contain hemopoietic tissue which functions in
- Produces red blood cells, white blood cells (neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils), and platelets.
- Found in the bone marrow of most bones, except for the skull, vertebrae, and ribs.
Lymphoid Tissue
- Produces lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell that plays a role in the immune system.
- Found in the bone marrow, spleen, thymus, and lymph nodes.
Structure of Hemopoietic Tissue

Hemopoietic tissue is highly organized and contains a variety of cell types.
- Stem cells:These are undifferentiated cells that can give rise to all types of blood cells.
- Progenitor cells:These are cells that have begun to differentiate but have not yet become fully mature blood cells.
- Mature blood cells:These are fully differentiated blood cells that are ready to enter the bloodstream.
The microenvironment of hemopoietic tissue plays a crucial role in supporting hemopoiesis. This microenvironment includes growth factors, cytokines, and other signaling molecules that regulate the production and differentiation of blood cells.
Regulation of Hemopoiesis
Hemopoiesis is a tightly regulated process that is controlled by a variety of factors.
- Growth factors:These are proteins that stimulate the production and differentiation of blood cells.
- Cytokines:These are proteins that regulate the immune system and also play a role in hemopoiesis.
- Hormones:These are chemical messengers that can influence hemopoiesis.
- The immune system:The immune system plays a role in regulating the production of white blood cells.
Clinical Applications
Hemopoietic tissue research has led to a number of clinical applications.
- Bone marrow transplantation:This procedure involves transplanting healthy bone marrow into a patient with a damaged or diseased bone marrow.
- Stem cell therapy:This is a promising new treatment approach that involves using stem cells to repair damaged tissues or organs.
FAQ Compilation
What is the primary function of hemopoietic tissue?
Hemopoietic tissue produces all types of blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Which bones contain hemopoietic tissue?
Hemopoietic tissue is primarily found in the bone marrow of flat bones, such as the sternum, ribs, and pelvis.
How is hemopoiesis regulated?
Hemopoiesis is regulated by a complex network of growth factors, cytokines, and hormones that control the production and differentiation of blood cells.