Label the Civil War battles worksheet answers is an invaluable resource for students and history enthusiasts seeking to delve deeper into the pivotal battles that shaped the course of American history. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the worksheet, its structure, content, and significance, empowering learners to grasp the complexities of the Civil War and its lasting impact.
Through an engaging analysis of the worksheet’s key concepts and skills, this guide illuminates the effectiveness of the resource in conveying historical information. Additionally, it presents a detailed HTML table that chronologically organizes the battles, providing insights into their dates, locations, and outcomes.
Civil War Battle Overview
The Civil War, a defining conflict in American history, erupted in 1861 between the Union (Northern states) and the Confederacy (Southern states) over issues of slavery, states’ rights, and economic disparities. The war’s major turning points included:
- Union victories at Gettysburg (1863) and Vicksburg (1863): These decisive battles crippled the Confederacy’s military power.
- Sherman’s March to the Sea (1864-1865): This scorched-earth campaign destroyed Confederate infrastructure and demoralized its troops.
- Lee’s surrender at Appomattox Court House (1865): This event marked the effective end of the war.
The Civil War’s consequences were far-reaching:
- Preservation of the Union: The war reaffirmed the supremacy of the federal government over individual states.
- Abolition of slavery: The war led to the ratification of the 13th Amendment, which abolished slavery.
- Reconstruction: The period following the war aimed to reunite the country and address the legacy of slavery.
Worksheet Analysis: Label The Civil War Battles Worksheet Answers
The worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of key Civil War battles. Its structure includes:
- Background information: Provides context on the causes and significance of the war.
- Table of battles: Lists major battles with information on their dates, locations, and outcomes.
- Maps: Visual aids depicting the geographical locations of battles.
- Discussion questions: Encourages critical thinking and analysis of the war’s events.
The worksheet effectively conveys information by using a clear and organized structure, engaging visuals, and thought-provoking questions. It aims to teach students about the key battles of the Civil War, their strategic importance, and their impact on the war’s outcome.
Battle Identification
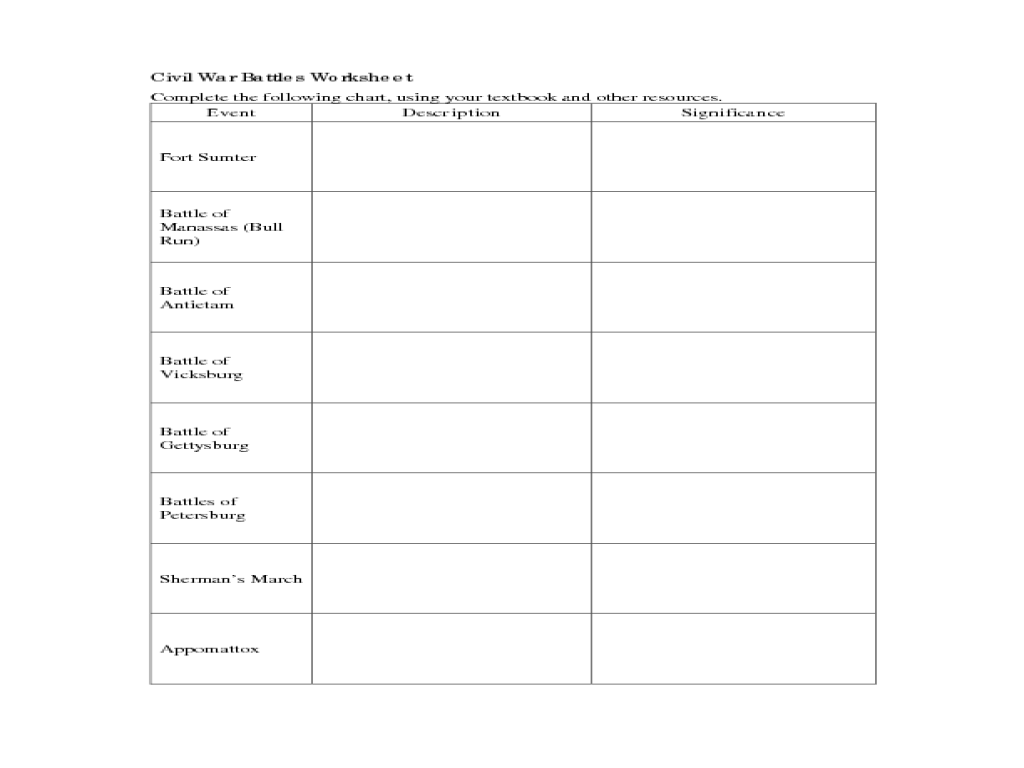
| Battle Name | Date | Location | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Battle of Bull Run | July 21, 1861 | Manassas, Virginia | Confederate victory |
| Battle of Antietam | September 17, 1862 | Sharpsburg, Maryland | Union victory |
| Battle of Gettysburg | July 1-3, 1863 | Gettysburg, Pennsylvania | Union victory |
| Battle of Vicksburg | May 18-July 4, 1863 | Vicksburg, Mississippi | Union victory |
| Sherman’s March to the Sea | November 15-December 21, 1864 | Atlanta, Georgia to Savannah, Georgia | Union victory |
| Battle of Appomattox Court House | April 9, 1865 | Appomattox Court House, Virginia | Confederate surrender |
Battle Significance
First Battle of Bull Run:
- Marked the first major battle of the Civil War.
- Boosted Confederate morale and shocked the Union.
Battle of Antietam:
- Halted Lee’s invasion of the North.
- Allowed Lincoln to issue the Emancipation Proclamation.
Battle of Gettysburg:
- Marked a turning point in the war, favoring the Union.
- Lee’s failed invasion of the North crippled the Confederacy.
Battle of Vicksburg:
- Gave the Union control of the Mississippi River.
- Cut off the Confederacy’s western supply lines.
Sherman’s March to the Sea:
- Devastated the Confederacy’s economy and infrastructure.
- Forced Lee to surrender at Appomattox Court House.
Battle of Appomattox Court House:
- Marked the effective end of the Civil War.
- Preserved the Union and led to the abolition of slavery.
Historical Context
Timeline of Events:
- 1860: Abraham Lincoln elected president.
- 1861: Southern states secede from the Union.
- 1863: Emancipation Proclamation issued.
- 1864: Sherman’s March to the Sea.
- 1865: Confederate surrender at Appomattox Court House.
Social, Economic, and Political Factors:
- Slavery: The primary cause of the war, dividing the nation over moral, economic, and political issues.
- States’ rights: Southern states argued for the right to maintain their own institutions, including slavery.
- Economic disparities: The North’s industrial economy clashed with the South’s agricultural economy.
Q&A
What is the purpose of the label the Civil War battles worksheet?
The worksheet aims to enhance students’ understanding of the major battles of the American Civil War, their significance, and their impact on the course of the conflict.
How does the worksheet help students learn about the Civil War?
The worksheet provides a structured approach to learning about the battles, including their dates, locations, outcomes, and strategic importance. It also encourages students to analyze the battles and their impact on the war.
What are the benefits of using the label the Civil War battles worksheet?
The worksheet offers several benefits, including improved comprehension of the Civil War battles, enhanced critical thinking skills, and a deeper understanding of the historical context of the conflict.
